Chinese scientists have developed a cell with a new blade-coating method and BTP-4Cl-12, a kind of acceptor that is a derivative of the Y6 acceptor, which is widely used in organic PV applications. The researchers also claim that the cells can maintain good efficiency levels, even if its surface is lightly expanded.
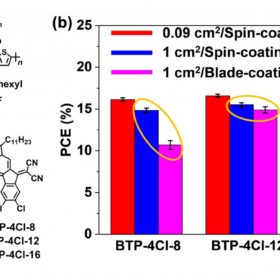
Researchers at the Chinese Academy of Sciences claim to have demonstrated a conversion efficiency of 17% in an organic PV cell with a small area of 0.09 cm2.
The cell is based on a new non-fullerene electron acceptor, which is said to be a new class of the Y6 non-fullerene acceptor that is widely used in research on organic solar cells.
The scientists developed the new BTP-4Cl-12 acceptor by optimizing the alkyl chains of BTP-4Cl, which is a derivative of the well-known Y6.
By using a blade-coating method, the scientists expanded the active area of the cell to 1.0 cm2 at a later stage. The device efficiency declined by 1.5%, which the researchers claim is still a very good level.
They also described the new acceptor as having balanced solution processability and aggregation features. “The blade-coating film showed a very good phase separation morphology, which contributed to the high carrier transport and suppressed charge recombination in the OPV cells,” the research team stated.
The paper, 17% efficiency organic photovoltaic cell with superior processability, was published in the National Science Review. It notes that the new non-fullerene acceptor has a suitable solubility and thus a desirable morphology.
The scientist found that the efficiency of the demonstrated spin-coated OPV devices can also be maintained with the presented scalable blade-coating processing technology.
Lắp đặt điện mặt trời Khải Minh Tech
https://ift.tt/2X7bF6x
0906633505
info.khaiminhtech@gmail.com
80/39 Trần Quang Diệu, Phường 14, Quận 3
Lắp đặt điện mặt trời Khải Minh Tech
https://ift.tt/2ZH4TRU
Không có nhận xét nào:
Đăng nhận xét