Building integrated PV has been described as a place where uncompetitive PV products attempt to go to market. But this may be unfair, says Björn Rau, the technology manager and deputy director of PVcomB at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin. Rau argues that the missing link to BIPV deployment lies at the intersection of the architectural community, construction industry, and PV manufacturers.
From pv magazine 12/2019
PV’s rapid growth over the last decade, to a global market of some 100 GWp installed annually, means some 350 to 400 million solar modules are produced and sold each year. However, their integration into buildings remains a niche market. According to a recent report published by the European Union Horizon 2020 research project PVSITES, only about two percent of the installed PV capacity was integrated into building skins in 2016. This meager figure is particularly remarkable when it is considered that more than 70% of energy produced worldwide is consumed in cities, and about 40 to 50% of all greenhouse gas emissions originate from urban areas.
To tackle both this greenhouse gas challenge and to promote on-site electricity generation, the European Parliament and the Council introduced the Directive 2010/31/EU on the energy performance of buildings with the concept of Nearly Zero Energy Buildings (NZEB) in 2010. The directive is applicable to all new buildings to be built from 2021 onwards. For new buildings that are to house public authorities the directive was applicable already at the start of this year.
There are no concrete actions specified to reach the NZEB status. Builder-owners can consider various aspects of energy efficiency such as insulation, heat recovery and electricity saving concepts. But as the overall energy balance of a building is the target of regulation, active energy production with or at the building appears to be indispensable to achieve NZEB standards.
Potential and challenges
The implementation of PV will undoubtedly play an important role in the design of future buildings or the retrofit of the existing building infrastructure. NZEB standards will be one driver of this, but it will not be alone. Building-Integrated PV (BIPV) can be used to activate existing areas or surfaces for the production of electricity. Thus, no additional space is required to bring more PV into urban areas. The potential for clean electricity produced with integrated PV is enormous. As the Becquerel institute found in 2016, the potential share of BIPV power generation in total power demand is more than 30% for Germany and even about 40% for more southern countries like Italy.
But, why do BIPV solutions still play only a marginal role in the solar business? And why are they so seldom considered in construction projects to date?
In order to answer these questions, the German research centre Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin (HZB) performed a needs analysis by organizing a workshop and engaging with stakeholders from all fields of BIPV last year. And the results show that it is not the technology itself that is lacking.
At the HZB workshop, many from the construction industry, performing both new-build or renovation projects admitted that a knowledge gap in terms of the potential of BIPV and enabling technologies exists. The majority of architects, planners and builder-owners simply do not have sufficient information about the technical and creative possibilities for the integration of PV into their projects. As a result, there are many reservations about BIPV, such as unalluring designs, high costs and a prohibitive level of complexity. In order to overcome these apparent misconceptions, the needs of architects and builder-owners must be placed front-and-center and an understanding as to how BIPV is perceived by these stakeholders brought into focus.
Function and style
BIPV is characterized by the fact that a solar module is an integral part of the building skin and hence becomes a multifunctional building element. Beside the generation of electricity, the module now has to take over the additional functions of the building skin.
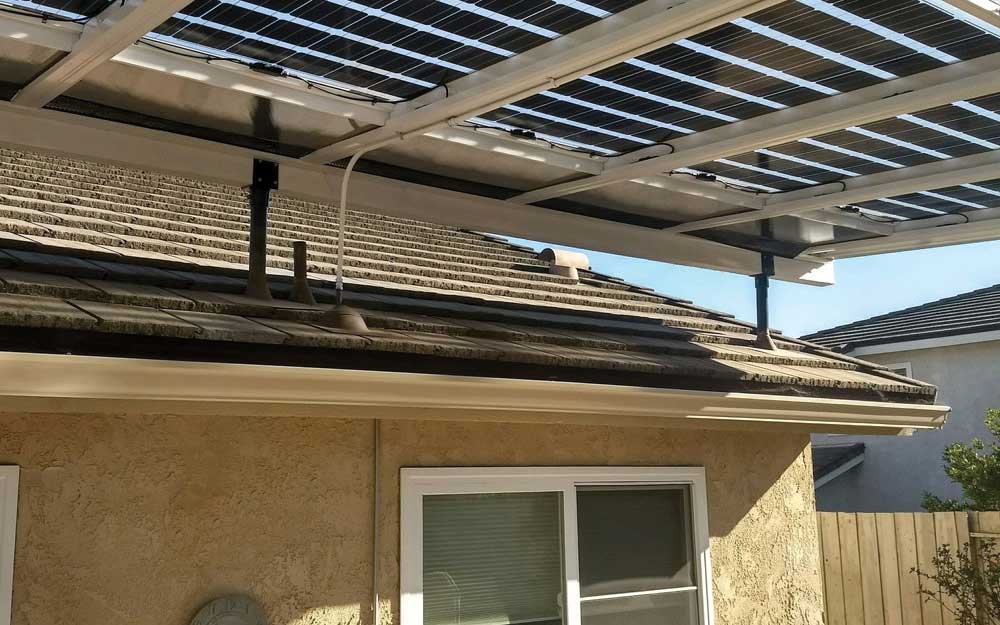
The diagram (right) illustrates some examples of different kinds of integration. Obviously, the best-known alternative to conventional rooftop installations are solar modules that are integrated both functionally and aesthetically directly into the roof. Thus, the modules not only generate electricity, they also act as roofing, protecting against weather. If they are visible, in the case of a pitched roof, the solar modules also influence the appearance of the building. The diversity of conventional roof elements also requires PV-active elements that have high variability in shape, color and appearance. Large-area, homogeneous glass-glass modules are needed, as well as small-sized systems like roof tiles, fitting perfectly in shape and color to conventional roof tiles.
Similar criteria are valid for solar modules used as façade elements, but here the aesthetic qualities are particularly important. There are different kinds of PV-active façades. Solar modules installed as ventilated cold façade can replace conventional elements of ventilated curtain walls quite easily. But solutions as warm façade elements are also possible, for instance directly stuck onto a façade. Beside the protection against weather, heat insulation or insulation against noise are additional attributes that a PV-active façade element can deliver.
Regarding to the aesthetic function of the façade elements, there are already different concepts on the market. Colored modules are available ranging from anthracite/black to grey, blue, green, yellow or even “golden”. These colors can be achieved, for instance, by the use of a special front glass that incorporates nano-sized layer structures. Importantly, the power output of this type of module is not prohibitively decreased, with more than 80% of the initial power output achieved when compared with a traditional module with transparent front glass.
An alternative to the use of this special front glass is ceramic printing. This technique achieves homogeneous colors along with another feature that architects like: the potential to print almost any structure or picture on top of the module. This feature can actually make the solar cells that comprise the module almost invisible to an observer. Such printing, however, does influence the final power output more strongly. But due to the almost complete invisibility of the solar cells, the technique can also be applied to high powered crystalline modules, and therefore perform as a building element of high aesthetic value and high power.
A third technique to create colored BIPV elements is the use of colored foils. This technology is less costly and, even more importantly, it allows for almost any color. Because of this feature, researchers from the Swiss Center for Electronics and Microtechnoloy (CSEM) were able to develop white solar modules. In principle, this development enables the “activation” of huge areas of conventional white façades which are present all over the world.
The integration of solar cells or modules into shading elements is an attractive method to combine sun protection and energy production. This can be achieved for instance by using glass with a very thin, homogeneous coverage of active photovoltaic material. Thin film techniques like organic semiconductors (OPV), CIGS (Copper-Indium-Gallium-Selenide/Sulphite), or thin film silicon are well suited for such applications.
Alternatively, semi-transparency can also be realized by the use of crystalline silicon cells if they are arranged in a glass-glass-module as a pattern or with larger gaps between the cells. This concept is used in systems in over-head-installations along with vertical glass façades. And it can also be implemented into movable shading installations which provide a reduction of sunlight at certain times of the day.
All of these approaches demonstrate the way in which BIPV solar modules can deliver additional functionality and address aesthetic concerns, making them more attractive to architects. But they are also accompanied by some level of reduced power output when compared to conventional, yield-optimized modules. Despite the power losses, the aesthetic and functional benefits make them attractive to the construction industry, which places a far lesser emphasis on optimization for power generation. Given this, BIPV elements should be benchmarked with respect to conventional, electrically inactive building elements.
Change of mindset
BIPV is different in many aspects from conventional rooftop solar systems, where neither a multifunctionality is required nor aesthetic aspects considered. Manufacturers need to rethink if they develop products designed for integration into building elements. Architects, builders and also the users of buildings initially expect the fulfilment of the conventional functions in a building skin. From their point of view the generation of electricity is an add-on property. In addition to that, developers of multifunctional BIPV elements have to consider the following aspects:
- Development of cost-effective, customized solutions for solar-active building elements with variable size, shape, color and transparency;
- Development of standards, and being attractive in price (ideally usable in the established planning tools, like Building Information Modelling (BIM);
- Integration of PV elements into novel façade elements by the combination of building materials and energy-producing elements;
- High resilience against temporary (local) shading;
- Long-term stability and degradation not only of power output but also with respect to the appearance (e.g. stability in color);
- Development of concepts for monitoring and maintenance, adapted to the individual situation onsite (considering the height of installation, the exchange of defective modules or façade element);
- And the compliance with the legal requirements like safety (including fire protection), construction law, energy law etc.
The issue of regulatory compliance is a challenge for all stakeholders. Both construction regulations and those in the energy sector typically depend strongly on local regulations. They are not only different between individual countries, but also deviate often significantly from each other in different states, cities or even local communities. However, it is not only the solar industry that needs to adapt.
The construction industry has to become aware of its responsibility to society as a whole. Both new buildings and renovation projects have to explicitly consider energy consumption and on-site generation. Building designers and those involved with construction have to be willing to work with new materials and elements providing the additional functionality of electricity generation. They also need to accept changes in their conventional planning processes, as electrical aspects have to be considered as early as the conceptual phase.
Closing the gap
The integration of PV into buildings is a challenge for all stakeholders. There is a gap, not only of knowledge about technologies and possibilities but also of cultures. In order to close these gaps, a bridge has to be built between the world of construction and the world of energy. Challenges have to be managed by all: architects and planners; manufacturers of materials and components; and also by R&D departments. These challenges are often new to all involved and influenced by existing prejudices. These are multifaceted challenges that, by their nature, can only be tackled together, and after accepting a change in thinking.
Based on discussions with the different BIPV stakeholders and recognizing these gaps, the HZB team recently started a novel initiative to promote BIPV. Combining its expertise in PV research, technology transfer and industrial collaborations with the perspective and network of architects and builder-owners and the network of a stakeholder’s association for BIPV, HZB founded a Consultancy Office for Building-integrated Photovoltaics – which goes by the acronym BAIP.
Co-funded by the German Helmholtz Association, BAIP addresses particularly the initial group of decision-makers for construction and renovation projects. In order to consider the real needs of the target group and to speak the language of it, the BAIP team consists not only of PV and knowledge transfer experts but also architects that can boast of a wealth of experience.
BAIP has been designed to provide a range of services to its customers. One particular service is the provision of individual, product-neutral and free-of-cost consultancy for architects, planners and builder-owners. Here, the focus is to provide initial information about the existing possibilities and opportunities, but also about obstacles and boundary conditions. The aim is to enable the target group to start considering and, in best case, realizing BIPV into their projects.
A second way to inform the architects is the collaboration with the architects associations, or chambers. Within the framework of mandatory, educational programs for architects, BAIP provides specific workshops and lectures about BIPV. A third tool is the organization of round tables with all BIPV stakeholders to foster the dialogue between them and reveal possible tasks for R&D teams.
The activities of BAIP have already generated a lot of interest. The team advises several individual requests per week, some of them with respect to very specific requests and some more general in nature. In addition, BAIP has organized its first in-house workshop in September which was fully subscribed. The response of the participants and the clients of the daily services confirms the demand of consultancy and the need for such a service.
About the author
Björn Rau is the co-initiator and head of BAIP, and the Deputy Director of the PVcomB, the Competence Center for Thin Film and Nanotechnology for Photovoltaics Berlin at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin. After completing his doctorate at Humboldt University Berlin, the physicist worked at HZB on the development of novel thin-film solar cells. Since 2009, as Head of Technology, he is responsible for setting up and operating the scientific and technical infrastructure of the technology transfer institute PVcomB.
Lắp đặt điện mặt trời Khải Minh Tech
https://ift.tt/2X7bF6x
0906633505
info.khaiminhtech@gmail.com
80/39 Trần Quang Diệu, Phường 14, Quận 3
Lắp đặt điện mặt trời Khải Minh Tech
https://ift.tt/2ZH4TRU